ABS
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) is a common thermoplastic polymer. Its glass transition temperature is approximately 105 °C. ABS is amorphous and therefore has no true melting point.
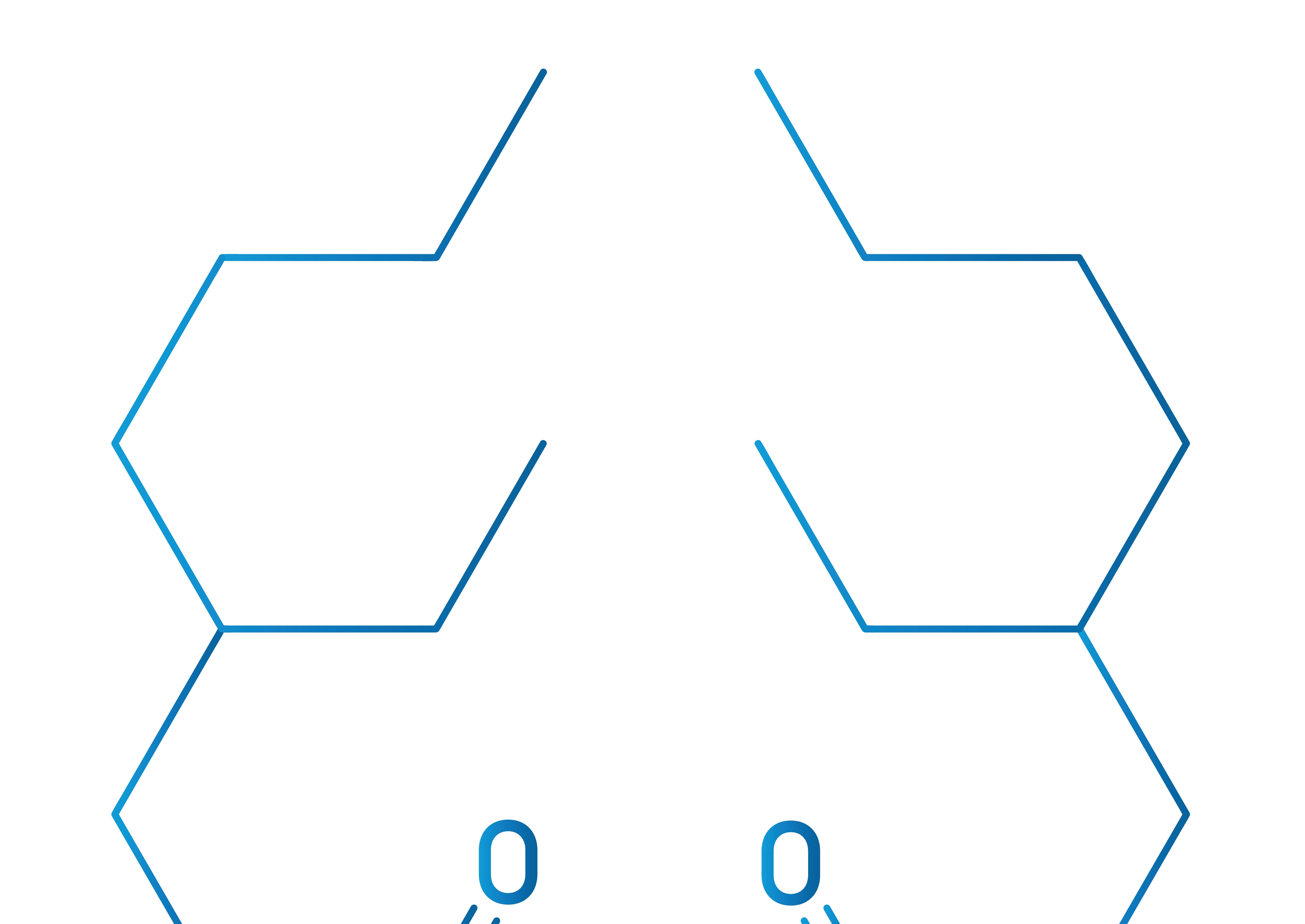
ABS is a terpolymer made by polymerizing styrene and acrylonitrile in the presence of polybutadiene. The proportions can vary from 15% to 35% acrylonitrile, 5% to 30% butadiene and 40% to 60% styrene. The result is a long chain of polybutadiene crisscrossed with shorter chains of poly(styrene-co-acrylonitrile). The nitrile groups from neighbouring chains, being polar, attract each other and bind the chains together, making ABS stronger than pure polystyrene. The acrylonitrile also contributes chemical resistance, fatigue resistance, hardness, and rigidity, while increasing the heat deflection temperature. The styrene gives the plastic a shiny, impervious surface, as well as hardness, rigidity, and improved processing ease.
ABS's light weight and ability to be injection moulded and extruded make it useful in manufacturing products such as drain-waste-vent (DWV) pipes, musical instruments, golf club heads, automotive components, drug delivery systens tracheal tubes, enclosures for electrical and electronic assemlies, luggage, toys. When extruded in filament, ABS plastic is a common material used in 3D Printers.